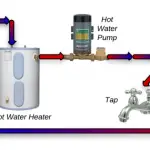
Once you have decided to have the water softener installed at your home, the next best thing that you need to check out is to find the right type of salt to be added to the water softener. That is where the confusion and chaos creep in. You have Blue, Green, and Yellow bags of water softener salts, and how to find the right one among them? What are the blue, green, and yellow salt bags, actually?
The Blue, green and Yellow salts refer to the types of salt, and there is nothing complicated about them. They are referred to by colour for the sake of identification. The Blue bag refers to coarse solar salt crystals, green bag refers to rust or iron content along a little manganese. The yellow bags contain the salt pellets. You can choose the right one based on your water softener built and the water hardness in your region.
What Types of Salts Are Available For Water Softeners?
There are basically three types of salts available for water softeners. Extra coarse solar salt or blue bags, pellets or yellow bags and rust or iron or green bags. Each of them has its own plus points and can be used for specific requirements.
Here we go with the explanation of the different types of salt used in water softeners. I have been using and recommending the different types of salts based on the water conditions at the treatment site. With an experience of over 10 years in the water treatment and water softener technology, I recommend the blue bags to be the best pick in most of the situations.

Extra Coarse Solar (Blue Bags)
The blue bag or the extra coarse solar salt is one of the most commonly used water softener salts. The quality of the blue bags salt can vary from one manufacturer to another, but it has been regarded as one of the cleaner and more acceptable grade of salt used in a water softener.
The best benefit that you stand to gain with the extra coarse solar salt is that it is availability quite readily. It can also be an easier option to work with when handling the bridge formation. However, the salt is never processed and can leave rings or dirty water inside your brine tank. You should clean your brine tank once in a couple of years.
Pellets (Yellow bags)
This is the second most common slat used in water softeners. The pellets are considered to be the most clean salt type. Some manufacturers add up a little additives in the form of cleansers to improve the performance of the water softener.
The cost of the pellets is generally on the higher side as they are processed. To convert them into salt. In some cases, you may notice that the pellets may dissolve and disintegrate over time. They are also likely to dry up and harden. This can happen in the case of lower water usage. If you face these issues with your water softener, it is advisable to switch to extra coarse solar salt or blue bag salt.
Rust or iron (Green bag)
If you have water with a higher level of iron or manganese content. The green bags include the pellets with an addition of either sodium-bisulfate or citric acid. If you find your water supply is extremely hard, it is a good idea to switch to a green bag.
The additives in the green bag help you dissolve and clean the stubborn iron and manganese from the water. They have been observed to be the highest on the cost side among all the types of salts used in water softeners.
Potassium Chloride
Potassium Chloride is one the excellent alternatives to Sodium Chloride and finds a widespread usage across several situations. If you have any health issues that do not permit using sodium salts, you can switch to Potassium chloride.
Potassium chloride also has a few health benefits and has been a recommended option in many cases. However, it does come with its own disadvantages – it is quite an expensive option as it is almost four to five times costlier than the sodium chloride.
What is the Difference Between Sodium and Potassium Chloride?
Potassium chloride and sodium chloride are both salts, and you would find them being used in several applications. While they have a few similarities, they also have a few differences.
Chemical composition: Potassium Chloride consists of potassium and chlorine, while sodium chloride has a composition of sodium and chlorine.
Taste: Sodium chloride has a salty taste and is used in food seasoning and a table salt. Potassium chloride, too, has a salty taste but tends to be a little bitter. It is used as a substitute salt
Health effects: sodium chloride is a nutrient and an essential element, but too much of its consumption can result in high blood pressure, stroke and heart diseases. Potassium chloride is also a necessary element and required for a proper muscle build. However, an excessive consumption can lead to issues with your kidney.
Uses: Sodium chloride is normally used for seasoning. It is also used in food preservatives and industrial applications such as water softening and de-icing roads. Potassium Chloride also finds its usage as a food seasoning agent and food preservative. It also finds being used in medical scenarios.
Solubility: Sodium chloride is readily soluble in water and does not need any effort to dissolve it in water.. On the other hand, Potassium Chloride is a little less soluble.
The table here should help you have a better understanding of the differences between Sodium chloride and potassium chloride:
| Difference | Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | Potassium Chloride (KCl) |
| Chemical formula | NaCl | KCl |
| Taste | Salty | Salty, slightly bitter |
| Health effects | High intake can lead to high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke | High intake can lead to kidney problems |
| Usages | Commonly used as a seasoning, food preservative, and in industrial applications such as water softening and de-icing roads | Used as a seasoning, food preservative, in medical applications such as intravenous fluids, and as a treatment for hypokalemia (low potassium levels) |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water | Less soluble in water compared to NaCl |
What Are The Rules For Choosing The Perfect Salt For Your Water Softener?
There are a few specific rules that you need to follow when choosing the right type of salt for your water softener.
Rule No 1: Never Use Rock salt
The rock salt is a mineral form of table salt. It may be a good pick for de-icing the roads or sidewalks, but it should never be used in a water softener. It is very much less refined and needs to be cleaner. The contaminants in the salt can leave a lot of debris and can create issues.
Always choose the high-quality salt. The extra coarse solar salt or the blue bags are interesting.
Rule No 2: Use any salt, but avoid running the water softener without salt
If you are out of salt, make sure that you have chosen any bag – either blue, green and yellow. Anyone among them will do, but never run the water softener without any salt. If you do not have any option, use any salt.
Rule No 3: Once you have a salt bag, make sure that you do not switch to any other bag
After you have chosen a salt bag and decided on it, you should continue with it and should not change it. If you have sufficient salt in the brine tank, continue with the same salt. Each of the different salt types comes with different dissolving rates, and changing them can result in the undesirable conditions like mushed salt or salt bridges.
Rule No 4: Do not switch the salt until it is completely empty
For any reason, if you are looking to switch your salt, make sure that you have emptied the salt in the brine tank. Mixing two different types of salt may not be a good idea. It can result in unwanted water conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Parting Thoughts
Choosing the right type of salt in your water softener would make it a formidable task and can be a daunting one at times. If you are confused about choosing between blue or yellow or green bags of salt, the choice of options that we have featured here is quite handy enough in understanding the proper details.








Add Comment